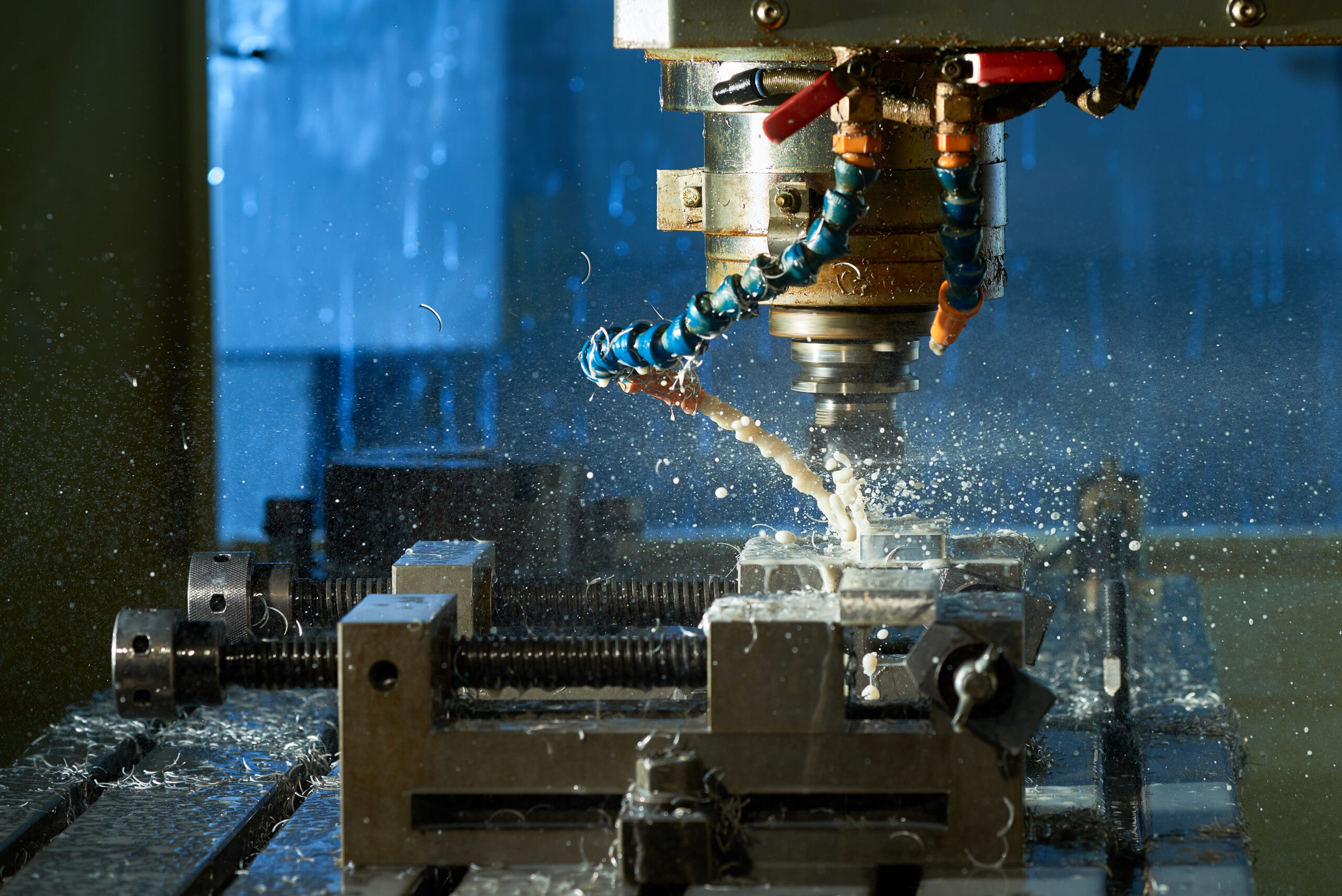

In today's fast-paced industrial world, CNC machining is one of the most widely used and reliable manufacturing methods. Known for its precision, versatility and efficiency, CNC machining has revolutionized how manufacturers create complex parts for industries like aerospace, medical, defense and optical.
If you're new to this technology or simply want a better understanding of how it works, this guide covers everything you need to know about the CNC machining process — from how it began to its real-world applications, advantages and what the future holds.
Table of Contents
What Is CNC Machining?
CNC machining stands for Computer Numerical Control machining — a manufacturing process where pre-programmed computer software controls the movement of tools and machinery. Unlike manual machining, where operators control the equipment by hand, CNC machining automates the process for consistent, precise and repeatable production.
CNC machines use a set of coded instructions, usually derived from a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) file, to direct the tools. These machines can perform a range of tasks including milling, turning, drilling and grinding with incredible accuracy.
A Brief History of CNC Manufacturing
The origins of CNC machining can be traced back to the 1940s and 1950s, when engineers started using punched tape to control simple machines. By the 1970s, advances in computer technology transformed this method into what we now recognize as modern CNC manufacturing.
Since then, technology has evolved rapidly. Today’s CNC machines can operate on up to five or more axes, handle complex geometries and deliver exceptional repeatability, making them indispensable in high-precision industries.
How the CNC Machining Process Works
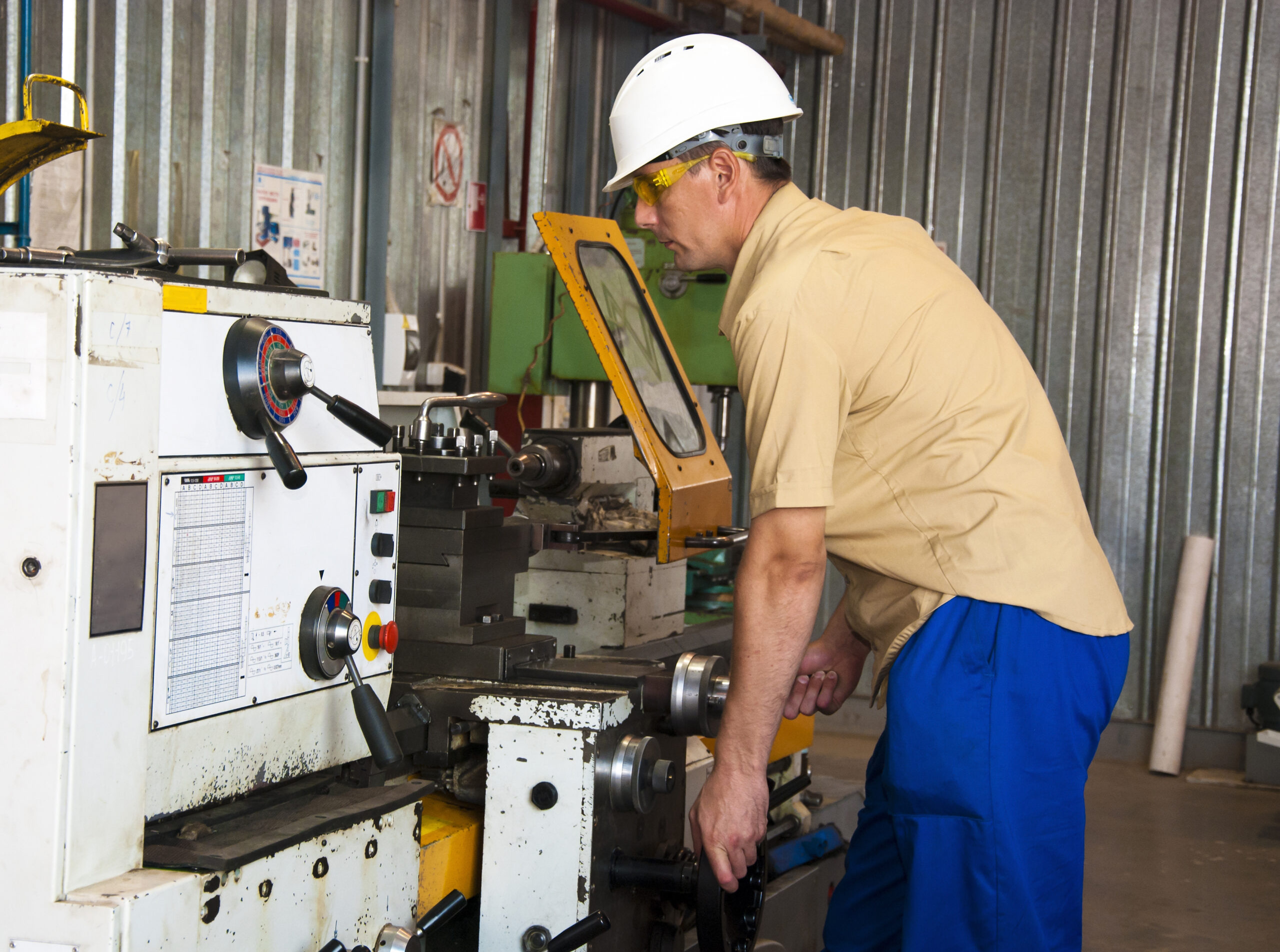

To fully understand the CNC manufacturing process, it helps to break it down step-by-step:
1. Designing the Part
The process begins with a detailed digital model of the part, created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This file includes exact dimensions, geometry and specifications.
2. Programming the Machine
Next, the CAD file is imported into Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software, which converts the design into a series of instructions that the CNC machine understands. These instructions include details about tool selection, speeds, feeds, cutting depth and sequence.
3. Setting Up the Machine
Before machining begins, an operator prepares the CNC machine by installing the necessary cutting tools and securing the raw material (often called a "workpiece"). This setup phase is crucial for ensuring that the machine operates efficiently and the final parts meet quality standards.
4. Executing the Program
The CNC machine reads the programmed instructions, which tells the machine’s motors and tools exactly how to move. The machine then performs the cutting, drilling, milling, turning or grinding operations automatically to remove material from the workpiece, following the programmed instructions precisely.
5. Conducting a Quality Inspection
Once machining is complete, the part undergoes inspection to make sure it meets the required tolerances, specifications and surface finish.
Types of CNC Machining Operations
CNC manufacturing can be applied in several ways, depending on the desired part geometry and material.
CNC Milling
The CNC milling process uses rotating cutting tools to remove material from the workpiece. These tools move along multiple axes in relation to the workpiece, allowing for greater precision and complexity. This process is great for creating slots, holes and complex 3D shapes.
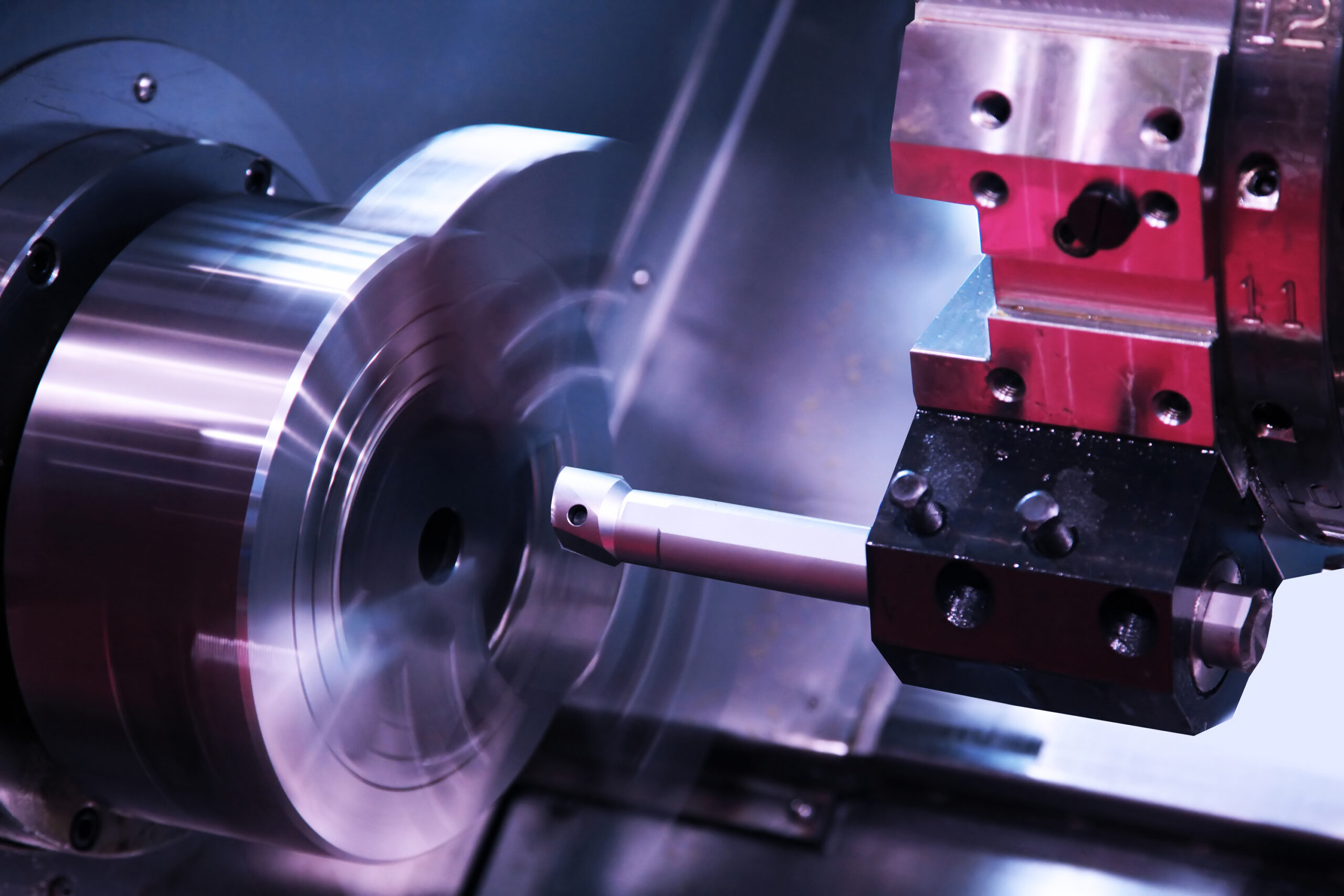

CNC Turning
Also known as CNC lathe machining, turning involves rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool removes material and shapes it. This method is ideal for cylindrical parts like shafts, pins and threaded components.
CNC Drilling
As the name suggests, this operation involves creating precise holes in the material by moving a drill bit vertically into the workpiece. CNC drilling offers excellent repeatability for parts requiring multiple holes.
CNC Grinding
The CNC grinding process uses abrasive wheels to achieve ultra-smooth finishes and tight tolerances, often used for high-precision components.
Common Materials Used in CNC Manufacturing
One of the major strengths of the CNC manufacturing process is its compatibility with a wide range of materials, including:
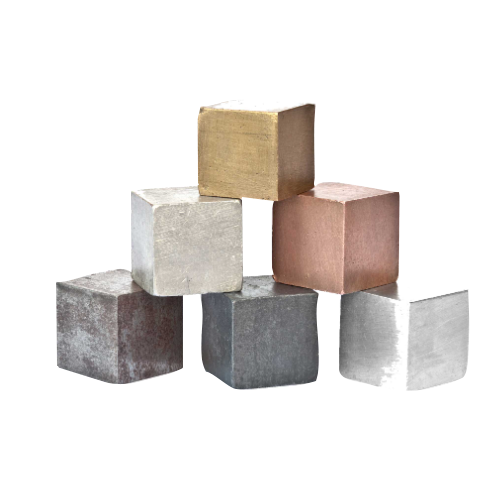

- Aluminum — Lightweight, corrosion-resistant and easy to machine.
- Stainless Steel — Strong, durable and ideal for high-stress environments.
- Titanium — Used in aerospace and medical applications for its strength-to-weight ratio.
- Brass & Copper — Naturally corrosion-resistant with high thermal and electrical conductivity.
- Plastics — Such as Delrin®, PEEK, UHMW and PVC, suitable for lightweight and non-conductive parts.
Applications of CNC Manufacturing Across Industries
CNC machining is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, playing a vital role in multiple sectors:
Aerospace Industry
Precision is non-negotiable in the aerospace industry. CNC manufacturing is used to produce structural components, brackets, turbine blades and fasteners that can withstand extreme stress and temperature changes.
Medical Industry
In the medical industry, surgical instruments, implants and diagnostic equipment all rely on CNC machining for biocompatibility, precision and durability.
Defense Industry
The defense sector uses CNC manufacturing to create components for weapons systems, armored vehicles and communication devices — demanding accuracy and material strength.
Optical Industry
In the optical industry, CNC machines manufacture tiny, intricate parts for lenses, adjustment screws and housings used in optical instruments like microscopes, telescopes and cameras.
Advantages of CNC Manufacturing
1. Unmatched Precision
CNC machines can maintain extremely tight tolerances, often down to ±0.0001 inches. This precision is crucial in industries like aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
2. Repeatability
Once a part is programmed, it can be reproduced with 100% consistency — ideal for both prototyping and full-scale production runs.
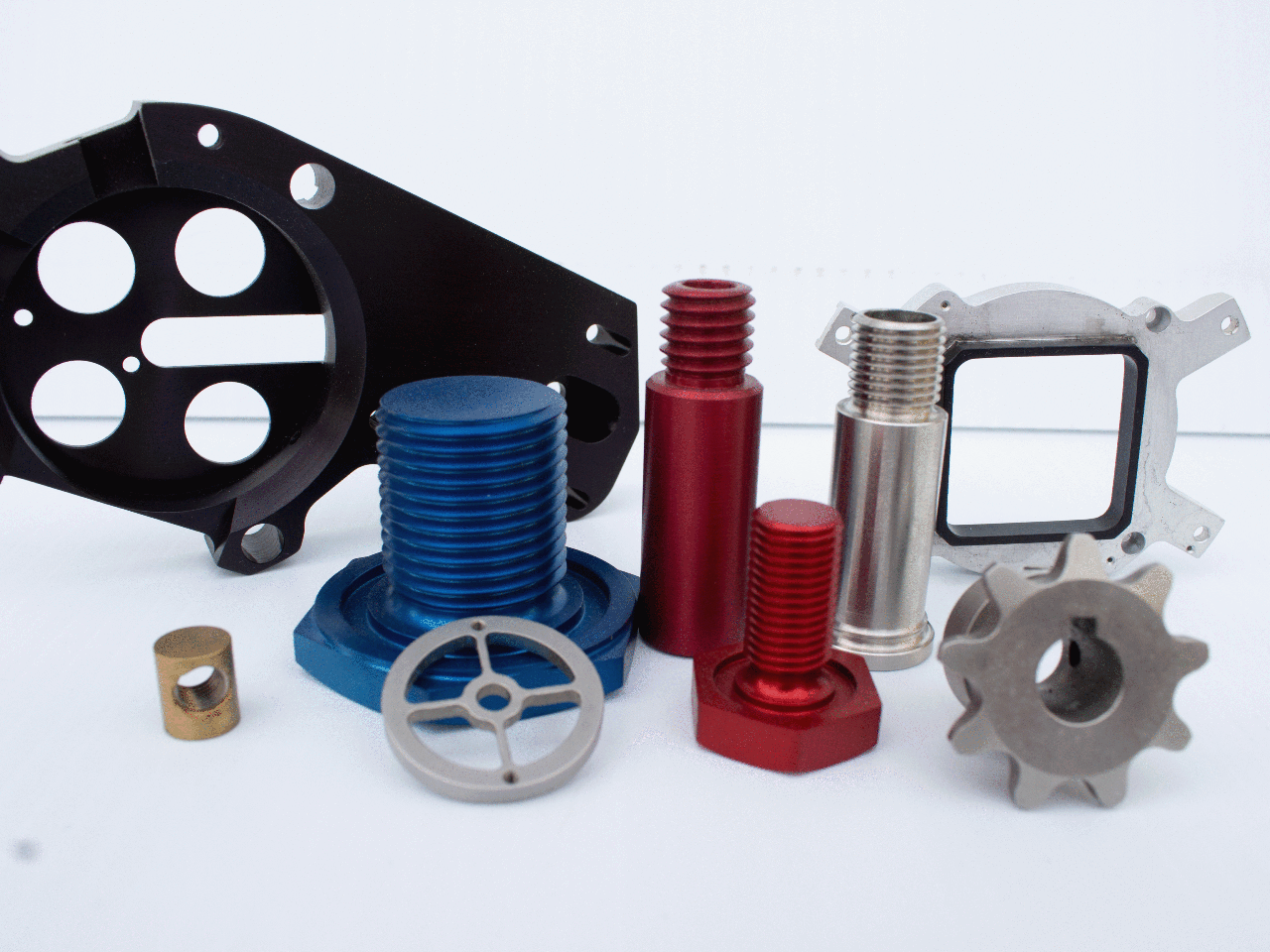
3. Versatility
From one-off custom parts to high-volume production, CNC machining can handle a wide variety of jobs with various materials and geometries.
4. Speed and Efficiency
CNC machining shortens production times and minimizes human error.
CNC Machining vs. Other Manufacturing Processes
How does CNC machining stack up against other common manufacturing methods?
| Method | Best For | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | Precise & complex geometries. Small-medium batches. | Higher per-unit cost for large volumes. |
| 3D Printing | Rapid prototyping. Complex geometries. | Limited material strength and surface finish. |
| Injection Molding | High-volume production. | High upfront tooling costs. Limited material options. |
| Casting | Large, heavy parts. | Less accurate. Poor for fine detail. |
How to Choose a CNC Machining Partner
When selecting a CNC machining service provider, consider the following:

Experience
Look for companies with experience in your industry and the ability to handle complex projects.
Capabilities
Do they offer multi-axis machining? Can they handle exotic materials?
Certifications
Reputable shops will have certifications such as ISO 9001 or AS9100, indicating a commitment to quality and compliance.
Material Knowledge
Shops like P4Swiss/Lindel CNC Machining specialize in manufacturing non-ferrous and exotic materials — offering valuable guidance for material selection.
Customer Support
Clear communication and transparency during quoting, production and delivery are essential for a smooth process.
Future Trends in CNC Manufacturing
CNC manufacturing continues to evolve with advancements such as:
- Machine Learning: Optimizing tool paths and improving predictive maintenance.
- Automation and Robotics: Enhancing productivity and reducing labor costs.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Helping manufacturers track machine performance and part quality in real-time.
Why CNC Machining Matters
As one of the most reliable and precise manufacturing methods, CNC machining is here to stay. Its ability to produce complex parts quickly, accurately and consistently makes it essential for companies seeking high-quality, dependable components.
Whether you're developing a new prototype, scaling your production or working with exotic materials, understanding the CNC machining process helps you make smarter, more efficient decisions.
At P4Swiss/Lindel CNC Machining, we specialize in delivering top-tier CNC machined parts using advanced equipment and decades of experience. Reach out today to learn how our team can help bring your next project to life.
Ready to Start Your CNC Machining Project?
If you have any questions or would like to submit a CNC request for quote (RFQ), please do not hesitate to contact Tony Torrez at tony@p4swisslindel.com, call us at (520) 792-3160 or click the “Request a Custom CNC Quote Today” button below.